What You Need to Know About Cheese and the Low FODMAP Diet
Cheese comes in all shapes, sizes, flavors, and ages. Good cheese can be an amazing flavor enhancer in all kinds of recipes from savory to sweet. It’s also delicious on its own. But cheese has lactose and I’m on a low FODMAP diet. Doesn’t that mean it’s off-limits for me??
No, it does not! Read on to learn why and to understand how to identify the best cheeses for you to enjoy.
According to Monash University, a dairy product qualifies as low FODMAP if its lactose content is 1 gram or less per serving. This can be determined by assessing the Total Carbs, which includes both Carbohydrates and Sugars, as indicated on the cheese label. This is great to know because it means, whether a cheese has undergone lab testing or not, you can gauge its FODMAP content by examining the nutrition label.
If the Total Carbs on the nutrition label amount to 1 gram or less per serving, you can reasonably conclude that the dairy product is low FODMAP per serving. This aligns with Monash University's guideline of a low FODMAP serving containing 1 gram or less of lactose.
Individuals with IBS are often advised to adopt a "lactose-free" approach, leading to the exclusion of milk and cheese from their diets. However, it's important to note that a low FODMAP diet is not synonymous with being entirely lactose-free. (While some people with IBS may also be sensitive to dairy itself, this is a different issue.)
Nevertheless, not all cheeses are created equal in terms of their compatibility with the low FODMAP diet. This article aims to serve as a helpful guide, navigating you through the intricacies so you can make informed choices that align with both your preferences and your gut health.
Can You Eat Cheese on a Low FODMAP Diet?
Navigating the FODMAP content of cheese can be a bit intricate, but fear not – by the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of what you need to consider when selecting your cheese, whether it's undergone lab testing or not.
Numerous cheeses have been tested for their FODMAP content, and you can easily access this information through the Monash App on your phone. To make things even more straightforward, here's a list of cheeses that have been tested and confirmed to be low FODMAP in a serving size of 1.4 ounces (40 grams):
Brie
Cheddar
Feta
Goat cheese (such as Montrachet)
Havarti
Monterey Jack
Mozzarella
Swiss
What About Cheese That Hasn’t Been Tested?
Now, let's address the cheeses that haven't undergone lab testing, which includes some of my favorites, such as blue cheese, Gruyere, Jarlsberg, Parmesan, Fontina, and Provolone just to name a few. You are probably wondering if these cheeses are on the Low FODMAP menu.
The answer is: YES!
You absolutely can include these cheeses in your diet. As always, the key is to be a vigilant label reader and remember you’re looking for total carbohydrates and relative serving size.
It's worth noting that when you purchase cheese from a specialty cheese store, the cheese is typically cut to order and won't carry the nutrition label. What you learn from reading labeled cheese can be applied to these cut-to-order cheeses as well. Just keep serving sizes and weights in mind.
Decoding FODMAPs In Cheese
When it comes to cheese and FODMAPs, the primary concern is lactose. Learn more about Lactose and its effect on those of us with IBS in this excellent article written by my brilliant sister, Sarah Aitken, RN, MS, WHNP/FNP, MHP, NBC-HWC.
Here's the key to figuring out the serving size of untested cheese yourself: if the Total Carbohydrates and/or Total Sugars on the nutrition label amount to 1 gram or less per serving, you can confidently consider that the cheese is low FODMAP per serving. This aligns with Monash University's threshold for a low FODMAP serving regarding lactose, which is 1 gram per serving. So, by keeping an eye on these numbers, you can make informed choices about the FODMAP content in your cheese, ensuring a gut-friendly indulgence.
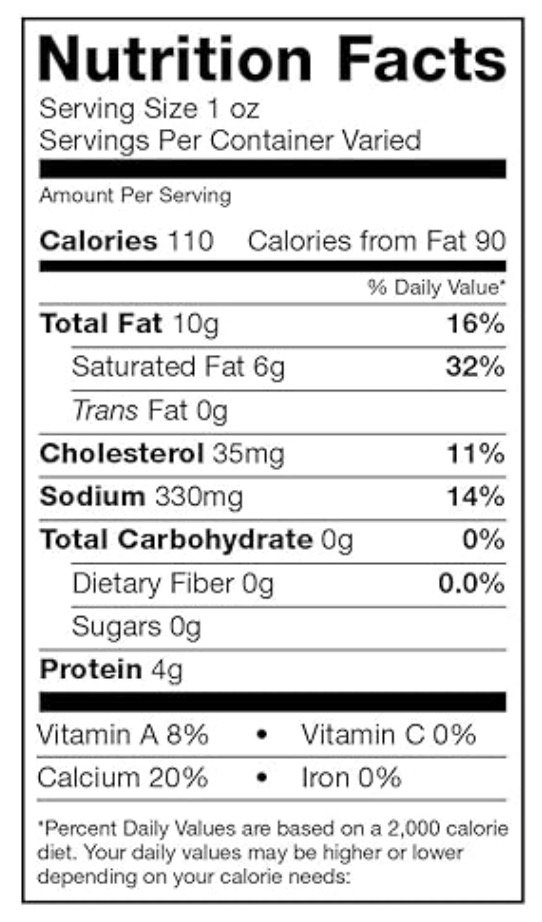
Read Those Cheese Labels!
Let's take a look at the label of traditional Danish blue cheese. Notice that the Total Carbohydrate per serving is listed as zero. Sometimes this may also be listed as < 1 (less than one). Zero does not mean there are zero carbs at any serving size but it DOES mean there is less than 1 gram of carbs per serving (which is 1 ounce in the case of most cheeses). This indicates that you can enjoy this particular blue cheese, adhering to the recommended serving size, even during the strict elimination phase of a Low FODMAP diet. And you may find, over time, you can tolerate larger serving sizes of cheese if you are not significantly triggered by lactose. (Need help figuring this out? Check out my Game Changer Program right here!)
In every case, when the Carbohydrates and Sugars—collectively referred to as Total Carbs—are under 1 gram per serving, they align with the low FODMAP designation established by Monash University, the gold standard for the FODMAP content of food.
If you come across blue cheese, Gruyere, or any other cheese in a recipe, a simple calculation of serving sizes will reveal whether the recipe falls within the low FODMAP category, specifically concerning the cheese. Whether you're referencing the nutrition label at home or doing this on the spot while shopping, a quick math check ensures you stay in tune with your FODMAP-friendly choices.
How Dairy Becomes Low FODMAP
Some dairy products are treated to reduce their lactose content, making them suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or those following a low FODMAP diet. These products are labeled “lactose-free” even though most of them do contain lactose but they have been augmented with enzymes to break the lactose down as you eat it. Processes such as fermentation, aging, and specific enzyme treatments can also break down lactose before it even gets to your mouth.
As cheese ages, bacteria and enzymes used in the fermentation process actually consume some of the lactose in the cheese to fuel the fermentation. This results in lower levels of lactose in the final product. So, in general, the longer a cheese is aged, the lower the lactose in the cheese. Both soft and hard cheeses undergo distinct changes as they age and they share the commonality of containing low FODMAP amounts. Examples of aged cheeses include cheddar, Gruyere, Brie, Swiss, Parmesan, and so many more.
So, eat and enjoy every bite because you can!